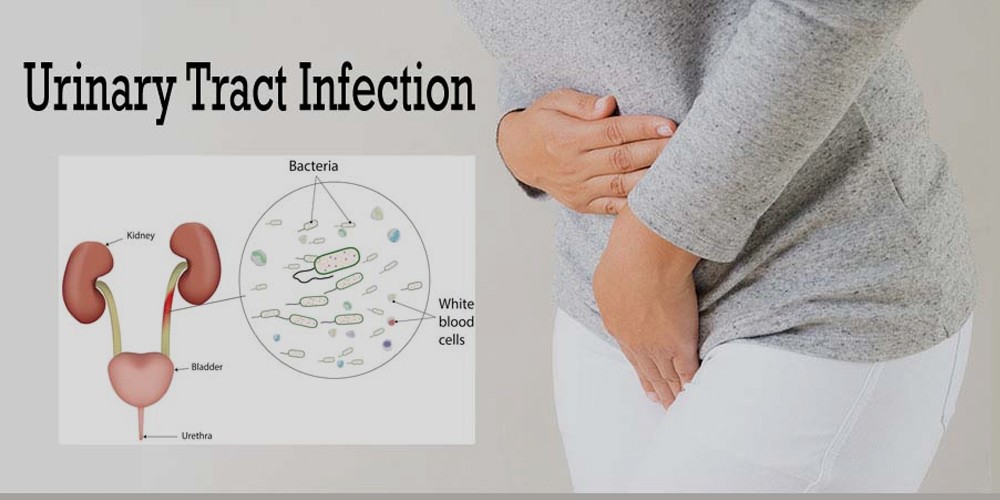
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common infections that affect the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. While anyone can get a UTI, they are more prevalent in women. Understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of UTIs can help manage and reduce the risk of these infections. Fosfomycin Tromethamine Packet 3 Gm to treat urinary tract infection and cystitis (bladder infection) in women.
What is an Urinary Tract Infection?
A UTI occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply. The most common bacteria causing UTIs is Escherichia coli (Fosfomycin Uses for UTI Treatment), which normally lives in the intestines. UTIs can be classified based on the part of the urinary tract they affect:
- Cystitis: Infection of the bladder.
- Urethritis: Infection of the urethra.
- Pyelonephritis: Infection of the kidneys, which is more severe.
Causes of UTIs
Several factors can increase the risk of developing a UTI:
- Female Anatomy: Women have a shorter urethra, making it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder.
- Sexual Activity: Increased sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Certain Types of Birth Control: Diaphragms and spermicidal agents can increase the risk of UTIs.
- Menopause: Changes in estrogen levels can alter the urinary tract, increasing susceptibility to infection.
- Urinary Catheters: Use of catheters can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Obstruction in the Urinary Tract: Kidney stones or an enlarged prostate can block the flow of urine and increase infection risk.
- Immune System Disorders: Conditions like diabetes can impair the immune system and increase the risk of UTIs.
Symptoms of UTIs
The symptoms of a UTI can vary depending on which part of the urinary tract is infected:
- Lower UTIs (Bladder and Urethra):
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate.
- A burning sensation during urination.
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine.
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
- Blood in the urine (hematuria).
- Pelvic pain, especially in women.
- Upper UTIs (Kidneys):
- Fever and chills.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Pain in the upper back and sides (flank pain).
Diagnosis of UTIs
To diagnose a UTI, a healthcare provider will typically:
- Ask About Symptoms: Discuss your symptoms and medical history.
- Perform a Physical Examination: Check for signs of infection.
- Urine Test: Analyze a urine sample to detect the presence of bacteria, white blood cells, or red blood cells.
- Imaging: In recurrent or severe cases, imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan may be used to examine the urinary tract.
Treatment of UTIs
The treatment of a UTI depends on the severity and location of the infection:
- Antibiotics: The primary treatment for UTIs is antibiotics. The type and duration of antibiotic treatment depend on the type of bacteria and the severity of the infection. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, and ciprofloxacin.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
Prevention of UTIs
There are several steps you can take to reduce the risk of developing a UTI:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps dilute urine and flush out bacteria.
- Urinate Frequently: Don’t hold urine for long periods. Urinate when you feel the need.
- Wipe Properly: Women should wipe from front to back to prevent bacteria from the anal region from spreading to the urethra.
- Empty Bladder After Sex: Urinating after sexual activity helps flush out bacteria introduced during intercourse.
- Avoid Irritating Products: Avoid using douches, powders, or deodorant sprays in the genital area, as they can irritate the urethra.
- Wear Cotton Underwear: Cotton underwear allows for better airflow and reduces moisture, which helps prevent bacterial growth.
Conclusion
Urinary tract infections are a common health issue, especially for women, but they can affect anyone. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications. By understanding the causes and taking preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of UTIs. Always consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment tailored to your specific condition.




